Added Value of Joint Action, a workshop methodology
Looking for ways to help stakeholders understand the benefits of multifunctional approaches and joint action? And make the next step towards cooperation? The workshop methodology ‘Added Value of Joint Action’ is developed to help you with this. In a structured and step-wise approach stakeholders find out what they can achieve alone and in cooperation, what the value is of different strategies, and ways for equal sharing of the winnings. The methodology used in this workshop tool is rooted in game theory.
Social dilemma of multifunctional concepts
Multifunctional approaches such as nature-based flood defences and multifunctional dikes combine flood safety with nature, recreation and housing. Combining functions potentially involves a win-win for the parties involved.
However often these situations present a social dilemma: cooperation may beneficial from the perspective of the group, but for the individual party cooperation is not the most attractive option. Multifunctional concepts require joint action, but due to present social dilemma’s cooperation will not come about without additional process support.
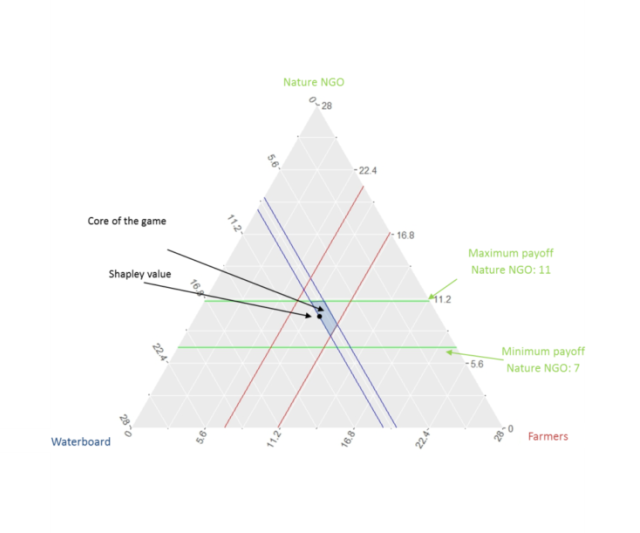
Stakeholders need to become familiar with what can be achieved when they cooperate and also how all parties involved can be satisfied with the chosen alternative.
Who benefits from the workshop?
The workshop is particularly useful in exploration of innovative strategies that are cross-sectoral and multifunctional and in investigating joint action possibilities. And is applicable in the fields of (multifunctional) flood risk management, spatial development and infrastructure projects and can be used by a wide range of stakeholders including governments, NGO’s, and private companies.
What is the result?
After the workshop, participants:
- Understand perspectives of the different stakeholders in their case
- Have insight in what they can achieve alone and what they can achieve by cooperation
- Know the (added) value of joint action and a multifunctional approach for their case
- Developed a strategic perspective for future actions
- Improved confidence and trust among participants
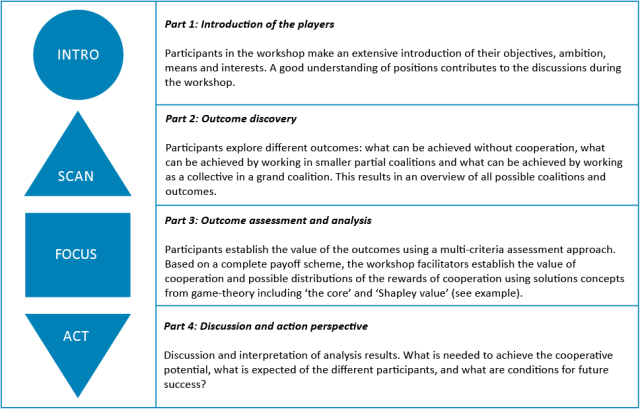
How is the workshop organised?
The workshop consists of four parts: 1) introduction, 2) outcome discovery 3) outcome assessment and analysis, and 4) discussion & action perspective.